|
|
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | |
| | |
| {{main menu}} | | {{main menu}} |
|
| |
| {{ArtBy| | | {{ArtBy| |
| | autore = Gianni Frisardi | | | autore = Gianni Frisardi |
| Line 6: |
Line 7: |
| | autore3 = Flavio Frisardi | | | autore3 = Flavio Frisardi |
| }} | | }} |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Abstract== | | ==Abstract== |
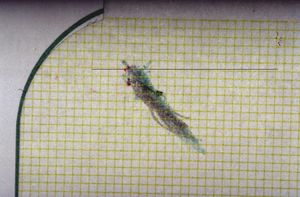
| [[File:Spasmo emimasticatorio.jpg|left|300x300px]]In the previous chapter, dedicated to the "[[Logic of medical language|Logic of Medical Language]]", we shifted focus from traditional clinical signs to an encrypted machine language, highlighting the innovative contributions of Donald E. Stanley, Daniel G. Campos, and Pat Croskerry. They emphasized the use of time as an information vector in diagnostics<ref>{{Cite book | autore = Stanley DE | autore2 = Campos DG | titolo = The logic of medical diagnosis | url = https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23974509/ | opera = Perspect Biol Med | anno = 2013 | DOI = 10.1353/pbm.2013.0019 | PMID = 23974509}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book | autore = Croskerry P | titolo = Adaptive expertise in medical decision making | url = https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/0142159X.2018.1484898 | opera = Med Teach | anno = 2018 | DOI = 10.1080/0142159X.2018.1484898 | PMID = 30033794}}</ref>. | | [[File:Spasmo emimasticatorio assiografia.jpg|left|300x300px]] |
| | Il documento "The Logic of the Classical Language - Masticationpedia" esplora il passaggio innovativo dalla comunicazione clinica tradizionale all'integrazione di logiche computazionali complesse nella medicina, con un focus particolare sulle implicazioni per la biologia craniofacciale. La narrazione evidenzia l'importanza delle tecnologie avanzate, come la sequenziazione genetica e le tecniche di imaging, per migliorare l'accuratezza diagnostica e l'efficacia dei trattamenti. |
|
| |
|
| This paradigm shift does not diminish the value of clinical history but enhances it by integrating a computational approach to validate medical diagnostics. "Craniofacial Biology" is explored comprehensively, with pivotal studies by Townsend and Brook challenging existing paradigms and proposing new clinical applications through interdisciplinary approaches.<ref>{{Cite book | autore = Townsend GC | autore2 = Brook AH | titolo = The face, the future, and dental practice | url = https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/adj.12157 | opera = Aust Dent J | anno = 2014 | DOI = 10.1111/adj.12157 | PMID = 24646132}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book | autore = Sperber GH | autore2 = Sperber SM | titolo = The genesis of craniofacial biology | url = https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/adj.12131 | opera = Aust Dent J | anno = 2014 | DOI = 10.1111/adj.12131 | PMID = 24495071}}</ref>Additionally, the role of epigenetics and phenomics in this field is underlined, offering new insights into dental and craniofacial anomalies through the genetic, epigenetic, and environmental interplay.<ref>{{Cite book | autore = Williams SD | autore2 = Hughes TE | autore3 = Adler CJ | autore4 = Brook AH | autore5 = Townsend GC | titolo = Epigenetics: a new frontier in dentistry | url = https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/adj.12155 | opera = Aust Dent J | anno = 2014 | DOI = 10.1111/adj.12155 | PMID = 24611746}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book | autore = Yong R | autore2 = Ranjitkar S | autore3 = Townsend GC | autore4 = Brook AH | autore5 = Smith RN | autore6 = Evans AR | autore7 = Hughes TE | autore8 = Lekkas D | titolo = Dental phenomics | url = https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/adj.12156 | opera = Aust Dent J | anno = 2014 | DOI = 10.1111/adj.12156 | PMID = 24611797}}</ref>This extensive review also incorporates diverse studies, illustrating the dynamic complexities of craniofacial development and the significant implications for future dental practices<ref>{{Cite book | autore = Peterkova R | autore2 = Hovorakova M | autore3 = Peterka M | autore4 = Lesot H | titolo = Three‐dimensional analysis of the early development of the dentition | url = https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/adj.12130 | opera = Aust Dent J | anno = 2014 | DOI = 10.1111/adj.12130}}</ref>. In summary, this chapter emphasizes not only the advanced computational methodologies enhancing diagnostic precision but also the critical interdisciplinary perspectives necessary for holistic patient care in craniofacial anomalies.
| | ==Introduzione== |
| <center><div class="colour-button">[[Special:UserLogin&returnto=Introduction+Page|Read more]]</div>
| | L'introduzione del documento pone le basi per comprendere il significativo impatto delle scienze dell'epigenetica e della fenomica nella medicina moderna. Queste scienze offrono una prospettiva innovativa sulla personalizzazione della cura medica, sottolineando come la comprensione dettagliata del patrimonio genetico e epigenetico di un individuo possa guidare lo sviluppo di trattamenti più efficaci per le anomalie craniofacciali. |
| </center>
| |
|
| |
|
| '''Mathematical Formalism:''' In this chapter, we revisit the clinical case of Mary Poppins, who has been suffering from Orofacial Pain for over ten years due to "Temporomandibular Disorder" (TMD). This section delves into the complexity of using Classic Language Logic to achieve a precise diagnostic definition. | | ==Impatto dell'Epigenetica e della Fenomica== |
| | Approfondendo, il testo discute come l'epigenetica e la fenomica stiano rivoluzionando la nostra comprensione delle malattie craniofacciali. Attraverso lo studio dell'interazione tra fattori genetici e ambientali, queste discipline aprono la strada a trattamenti altamente personalizzati, essenziali per affrontare le variazioni individuali nella biologia craniofacciale. |
|
| |
|
| '''Propositions''' The simplest propositions in logic can be combined using logical operators and quantifiers to construct complex logical statements, enhancing the precision and rigor required in mathematical and scientific reasoning. Key logical operators include: | | ==Logica Classica nella Diagnostica Medica== |
| *'''Conjunction''' (<math>\land</math>),
| | La sezione successiva esamina l'applicazione della logica classica nella diagnosi medica, utilizzando operatori logici e quantificatori per dedurre conclusioni diagnostiche precise. Questo metodo aiuta a sviluppare piani di trattamento mirati, particolarmente utili per condizioni complesse che interessano la regione craniofacciale. |
| *'''Disjunction''' (<math>\lor</math>),
| |
| *'''Negation''' (<math>\urcorner</math>),
| |
| *'''Implication''' (⇒),
| |
| *'''Logical consequence''' (<math>\vdash</math>),
| |
| *'''Universal quantifier''' (<math>\forall</math>),
| |
| *'''Existential quantifier''' (<math>\exists</math>).
| |
|
| |
|
| These tools help form the backbone of logical reasoning used to navigate complex diagnostic processes in medical practice.
| | ==Applicazioni Pratiche della Logica Formale== |
| | Questa parte del documento illustra casi pratici dove la logica formale è stata impiegata per risolvere complesse sfide diagnostiche in craniofacciale, mostrando l'efficacia di questo approccio nel trattamento di malattie complesse attraverso esempi specifici e studi di caso dettagliati. |
|
| |
|
| '''Proof by Contradiction:''' This method involves demonstrating that the negation of a proposition leads to a contradiction, thereby proving the original proposition under the principle of the "law of excluded middle". This fundamental aspect of classical logic asserts that a proposition must be true if its negation is false<ref>{{Cite book | author = Pereira LM | author2 = Pinto AM | title = Reductio ad Absurdum Argumentation in Normal Logic Programs | url = http://www-lia.deis.unibo.it/confs/ArgNMR/proceedings/ArgNMR-proceedings.pdf#page=100 | year = 2007 | publisher = Arg NMR | city = Tempe, Arizona - Caparica, Portugal}}</ref>.
| | ==Approccio Interdisciplinare== |
| | Il documento enfatizza l'importanza di un approccio interdisciplinare nel superare le sfide mediche, integrando conoscenze da diverse discipline scientifiche. Questo approccio è fondamentale per avanzare nel campo della cura del paziente, specialmente nelle complesse problematiche craniofacciali. |
|
| |
|
| | ==Verso un Linguaggio Logico Dinamico== |
| | La discussione si estende alla necessità di adottare un linguaggio logico più flessibile e dinamico in campo medico, capace di adattarsi alle complessità e alle sfumature della pratica clinica. Questo futuro prospettato enfatizza l'importanza di rimanere aperti e reattivi al paesaggio scientifico in evoluzione, garantendo che le pratiche mediche continuino a progredire in linea con le scoperte all'avanguardia. |
|
| |
|
| '''Predicates:'' Predicates are expressions that assert something about a set of elements, such as "all volleyball players are tall" <math>X</math> being volleyball players). They are used extensively to describe groups of patients or medical conditions, providing a structured way to apply logical reasoning in medical diagnoses.
| | ==Considerazioni Finali== |
| | | In conclusione, "The Logic of the Classical Language - Masticationpedia" presenta una visione avvincente del futuro, dove la fusione di logica computazionale, tecnologia avanzata e scienza medica inaugura una nuova era di diagnostica e cura del paziente. Il documento promuove un paradigma in cui il linguaggio medico, arricchito dal continuo progresso della conoscenza scientifica, porta a una precisione diagnostica senza precedenti e a un approccio al trattamento più efficace e personalizzato, stabilendo un nuovo standard nella cura dei pazienti, particolarmente nel campo della biologia craniofacciale. |
| Further diagnostic support is provided through the analysis of axiographic traces and surface electromyography, confirming the presence of TMD based on the observed asymmetry and functional abnormalities in masticatory muscles
| | <center><div class="colour-button">[[Special:UserLogin&returnto=Introduction+Page|Read more]]</div> |
| <ref>{{cite book | autore = Castroflorio T | autore2 = Talpone F | autore3 = Deregibus A | autore4 = Piancino MG | autore5 = Bracco P | titolo = Effects of a Functional Appliance on Masticatory Muscles of Young Adults Suffering From Muscle-Related Temporomandibular Disorder | url = https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15189308/ | opera = J Oral Rehabil | anno = 2004 | DOI = 10.1111/j.1365-2842.2004.01274.x | PMID = 15189308}}</ref>
| | </center> |
| <ref>{{cite book | autore = Maeda N | autore2 = Kodama N | autore3 = Manda Y | autore4 = Kawakami S | autore5 = Oki K | autore6 = Minagi S | titolo = Characteristics of Grouped Discharge Waveforms Observed in Long-term Masseter Muscle Electromyographic Recording: A Preliminary Study | url = http://ousar.lib.okayama-u.ac.jp/files/public/5/56938/20190821181112825794/73_4_357.pdf | opera = Acta Med Okayama | anno = 2019 | DOI = 10.18926/AMO/56938 | PMID = 31439959}}</ref>.
| |
| | |
| | |
| '''2nd Clinical Approach'''
| |
| | |
| This section presents further clinical evaluations including CT scans and electromyographic analysis which provide deeper insights into the structural and functional status of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). These findings are critical in confirming the diagnosis of TMD and understanding its impact on orofacial pain.
| |
| | |
| '''Propositions in the Dental Context'''
| |
| | |
| In an attempt to apply mathematical formalism to interpret the dentist's diagnostic conclusions using classical logic language, we define the following predicates: | |
| *<math>x \equiv</math> Normal patients (where "normal" refers to patients commonly encountered in a specialist setting)
| |
| *<math>A(x) \equiv</math> Presence of bone remodeling with detected osteophyte from stratigraphic exams and condylar CT
| |
| *<math>B(x)\equiv</math> Temporomandibular Disorders (TMD) resulting in orofacial pain (OP)
| |
| *<math>\mathrm{a}\equiv</math> Specific patient: Mary Poppins
| |
| | |
| We establish that for every normal patient <math>\mathrm{\mathcal{A}}(\text{x})</math>, if they test positive for the TMJ radiographic examination <math>\mathrm{\mathcal{A}}(\text{x})</math> [see Figures 2 and 3], then they are affected by TMD <math>\rightarrow\mathrm{\mathcal{B}}(\text{x})</math>. Consequently <math>\vdash</math> if Mary Poppins tests positive (and is considered a "normal patient") for the TMJ radiographic exam <math>A(a)</math>, it follows that she too is affected by TMD <math>\rightarrow \mathcal{B}(a)</math>. This can be formally expressed as:
| |
| | |
| {|
| |
| |<math>{a \in x \mid \forall \text{x} ; A(\text{x}) \rightarrow {B}(\text{x}) \vdash A( a)\rightarrow B(a) }</math>
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |<math>(1)</math>
| |
| |-
| |
| | |
| |}
| |
| | |
| To verify the truthfulness of this proposition, we resort to proof by contradiction. If the negation of the proposition generates a contradiction, we can conclude that the original hypothesis of the dentist is correct:
| |
| | |
| {|
| |
| |<math>\urcorner{a \in x \mid \forall \text{x} ; A(\text{x}) \rightarrow {B}(\text{x}) \vdash A( a)\rightarrow B(a) }</math>
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |<math>(2)</math>
| |
| |-
| |
| | |
| |}
| |
| '''Propositions in the Neurological Context'''
| |
| | |
| Suppose the neurologist contests conclusion (1), arguing that Mary Poppins does not suffer from TMD or that, at least, TMD is not the primary cause of her Orofacial Pain. Instead, he hypothesizes that Mary suffers from neuromotor type Orofacial Pain (<sub>n</sub>OP), classifying her not as a 'normal patient' but as a 'specific patient' (atypical for the dental specialist).
| |
| | |
| The neurologist's position can be formalized as follows:
| |
| {|
| |
| |<math>{a \not\in x \mid \forall \text{x} ; A(\text{x}) \rightarrow {B}(\text{x}) \and A( a)\rightarrow \urcorner B(a) }</math>
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |<math>(3)</math>
| |
| |-
| |
|
| |
|
| |}
| |
|
| |
|
| To validate this hypothesis through proof by contradiction, consider its negation:
| |
| {|
| |
| |<math>\urcorner{a \not\in x \mid \forall \text{x} ; A(\text{x}) \rightarrow {B}(\text{x}) \and A( a)\rightarrow \urcorner B(a) }</math>
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |}
| |
|
| |
|
| ===Compatibility and Incompatibility of Statements===
| | [[Category:Medical Innovations]] |
| The complexity arises when the dentist presents a series of statements based on clinical reports, such as stratigraphy and computed tomography (CT) of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), indicating an anatomical flattening of the joint, axiography of the condylar paths with a reduction of cinematic convexity, and an electromyographic (EMG) interference pattern showing asymmetry on the masseters. These evidences can be considered co-causes of damage to the temporomandibular joint and, consequently, responsible for "Orofacial Pain".
| | [[Category:Craniofacial Biology]] |
| | |
| Documents, reports, and clinical evidence can be used to make the neurologist's statement incompatible and support the dentist's diagnostic conclusion. To do this, we present some logical rules that describe compatibility or incompatibility according to classical language logic:
| |
| #A set of sentences <math>\Im</math> and a number <math>n\geq1</math> of other sentences or statements <math>(\delta_1,\delta_2,.....\delta_n \ )</math> are logically compatible if, and only if, their union <math>\Im\cup{\delta_1,\delta_2.....\delta_n}</math> is coherent.
| |
| # A set of sentences <math>\Im</math> and a number <math>n\geq1</math> of other sentences or statements <math>(\delta_1,\delta_2,.....\delta_n \ )</math> are logically incompatible if, and only if, their union <math>\Im\cup{\delta_1,\delta_2.....\delta_n}</math> is incoherent.
| |
| | |
| Let's examine this concept with practical examples. The dentist presents the following statement:
| |
| | |
| <math>\Im</math>: Following the personalized techniques suggested by Xin Liang et al. that focuses on the quantitative microstructural analysis of the bone value fraction, trabecular number, trabecular thickness, and trabecular separation on each slice of a TMJ CT, it appears that Mary Poppins is affected by Temporomandibular Disorders (TMDs) and the consequence causes orofacial pain.
| |
| | |
| However, to further confirm the diagnosis, the dentist presents a series of additional assertions that should pass the compatibility filter described above, thus establishing a coherent basis for the diagnosis of TMD in Mary Poppins.
| |
| | |
| <math>\delta_1=</math> Bone remodeling: The flattening of the axiographic traces shown in Figure 5 indicates the joint remodeling of Mary Poppins' right TMJ. This report can be related to a series of research and articles confirming how malocclusion can be associated with morphological changes of the temporomandibular joints, particularly if related to age. Indeed, the presence of chronic malocclusion can aggravate the scenario of bone remodeling.
| |
| | |
| <math>\delta_2=</math> Sensitivity and Specificity of the Axiographic Measurement: A study was conducted to evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of the data obtained from a sample of patients with temporomandibular joint disorders, using the ARCUSdigma axiographic system. The results showed a sensitivity of 84.21% for the right TMJ and 92.86% for the left TMJ, with a specificity of 93.75% and 95.65%, respectively.
| |
| | |
| <math>\delta_3=</math>...................<center><div class="colour-button">[[Special:UserLogin&returnto=Introduction+Page|Read more]]</div>
| |
| </center>
| |
| {{bib}}
| |

 Change language
Change language

[[|German]]

[[|Spanish]]

[[|French]]

[[|Italian]]
'The logic of the classical language'
Abstract
Il documento "The Logic of the Classical Language - Masticationpedia" esplora il passaggio innovativo dalla comunicazione clinica tradizionale all'integrazione di logiche computazionali complesse nella medicina, con un focus particolare sulle implicazioni per la biologia craniofacciale. La narrazione evidenzia l'importanza delle tecnologie avanzate, come la sequenziazione genetica e le tecniche di imaging, per migliorare l'accuratezza diagnostica e l'efficacia dei trattamenti.
Introduzione
L'introduzione del documento pone le basi per comprendere il significativo impatto delle scienze dell'epigenetica e della fenomica nella medicina moderna. Queste scienze offrono una prospettiva innovativa sulla personalizzazione della cura medica, sottolineando come la comprensione dettagliata del patrimonio genetico e epigenetico di un individuo possa guidare lo sviluppo di trattamenti più efficaci per le anomalie craniofacciali.
Impatto dell'Epigenetica e della Fenomica
Approfondendo, il testo discute come l'epigenetica e la fenomica stiano rivoluzionando la nostra comprensione delle malattie craniofacciali. Attraverso lo studio dell'interazione tra fattori genetici e ambientali, queste discipline aprono la strada a trattamenti altamente personalizzati, essenziali per affrontare le variazioni individuali nella biologia craniofacciale.
Logica Classica nella Diagnostica Medica
La sezione successiva esamina l'applicazione della logica classica nella diagnosi medica, utilizzando operatori logici e quantificatori per dedurre conclusioni diagnostiche precise. Questo metodo aiuta a sviluppare piani di trattamento mirati, particolarmente utili per condizioni complesse che interessano la regione craniofacciale.
Applicazioni Pratiche della Logica Formale
Questa parte del documento illustra casi pratici dove la logica formale è stata impiegata per risolvere complesse sfide diagnostiche in craniofacciale, mostrando l'efficacia di questo approccio nel trattamento di malattie complesse attraverso esempi specifici e studi di caso dettagliati.
Approccio Interdisciplinare
Il documento enfatizza l'importanza di un approccio interdisciplinare nel superare le sfide mediche, integrando conoscenze da diverse discipline scientifiche. Questo approccio è fondamentale per avanzare nel campo della cura del paziente, specialmente nelle complesse problematiche craniofacciali.
Verso un Linguaggio Logico Dinamico
La discussione si estende alla necessità di adottare un linguaggio logico più flessibile e dinamico in campo medico, capace di adattarsi alle complessità e alle sfumature della pratica clinica. Questo futuro prospettato enfatizza l'importanza di rimanere aperti e reattivi al paesaggio scientifico in evoluzione, garantendo che le pratiche mediche continuino a progredire in linea con le scoperte all'avanguardia.
Considerazioni Finali
In conclusione, "The Logic of the Classical Language - Masticationpedia" presenta una visione avvincente del futuro, dove la fusione di logica computazionale, tecnologia avanzata e scienza medica inaugura una nuova era di diagnostica e cura del paziente. Il documento promuove un paradigma in cui il linguaggio medico, arricchito dal continuo progresso della conoscenza scientifica, porta a una precisione diagnostica senza precedenti e a un approccio al trattamento più efficace e personalizzato, stabilendo un nuovo standard nella cura dei pazienti, particolarmente nel campo della biologia craniofacciale.