Difference between revisions of "'Logic of medical language'"
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{main menu}} | {{main menu}} | ||
{{ArtBy| | {{ArtBy| | ||
| autore = Gianni Frisardi | | autore = Gianni Frisardi | ||
| Line 8: | Line 9: | ||
== Abstract == | == Abstract == | ||
[[File:Atm1 sclerodermia.jpg|left|300px]] | [[File:Atm1 sclerodermia.jpg|left|300px]] | ||
The | "The document 'Logic of Medical Language - Masticationpedia' examines the complexities of medical language and its potential for ambiguity, which can lead to misinterpretation and diagnostic errors. By analyzing a clinical case, it stresses the necessity of formal logic in medical terminology to ensure accurate interpretations. The document outlines various examples of how different medical professionals might understand the same condition differently, leading to varied diagnoses. | ||
Key topics covered include the inherent ambiguity in medical language, a detailed clinical case of a patient named Mary Poppins, the concept of 'encrypted machine language' used in brain and medical communications, and the nuanced meanings of medical terms depending on context and user intent. The document concludes with a call for a paradigm shift in medical diagnostics from symptom-based to a more comprehensive understanding of diseases using 'encrypted machine language.'" | |||
== | ==Medical language is an extended natural language== | ||
This section discusses the semantic challenges in medical language, particularly when traditional natural language intersects with technical medical terminology. It highlights the differences between natural and formal languages, noting that while natural languages evolve organically, formal languages like mathematics are designed with clear rules. The text underlines the ambiguity in terms such as "orofacial pain," which can be interpreted differently depending on the medical specialty involved. This ambiguity is problematic because it can lead to misdiagnosis or conflicting treatments. | |||
The clinical case presented, concerning a patient named Mary Poppins, illustrates the complexities of diagnosing conditions like temporomandibular disorders (TMD) and neuropathic orofacial pain (nOP). The narrative shows how various specialists might interpret the same symptoms differently, leading to multiple diagnoses. The case emphasizes the importance of a multidisciplinary approach and the need for precise language to reduce diagnostic errors.<ref>{{cita libro | |||
| autore = Tanaka E | |||
| autore2 = Detamore MS | |||
| autore3 = Mercuri LG | |||
| titolo = Degenerative disorders of the temporomandibular joint: etiology, diagnosis, and treatment | |||
| url = https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18362309 | |||
| opera = J Dent Res | |||
| anno = 2008 | |||
| ISBN = | |||
| DOI = 10.1177/154405910808700406 | |||
| oaf = | |||
| PMID = 18362309 | |||
}}</ref><ref>{{cita libro | |||
| autore = Roberts WE | |||
| autore2 = Stocum DL | |||
| titolo = Part II: Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)-Regeneration, Degeneration, and Adaptation | |||
| url = https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29943316 | |||
| volume = | |||
| opera = Curr Osteoporos Rep | |||
| anno = 2018 | |||
| ISBN = | |||
| DOI = 10.1007/s11914-018-0462-8 | |||
| oaf = | |||
| PMID = 29943316 | |||
}}</ref><ref>{{cita libro | |||
| autore = Lingzhi L | |||
| autore2 = Huimin S | |||
| autore3 = Han X | |||
| autore4 = Lizhen W | |||
| titolo = MRI assessment and histopathologic evaluation of subchondral bone remodeling in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: a retrospective study | |||
| url = https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30122441 | |||
| volume = | |||
| opera = Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol | |||
| anno = 2018 | |||
| ISBN = | |||
| DOI = 10.1016/j.oooo.2018.05.047 | |||
| oaf = | |||
| PMID = 30122441 | |||
}}</ref> | |||
== | ==Clinical approach== | ||
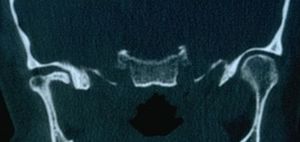
This section uses images to illustrate the clinical manifestations in the patient Mary Poppins, who suffers from orofacial pain and has undergone various medical evaluations that demonstrate the physical changes associated with her condition. | |||
The analysis of 'meaning' in medical terminology is complex and multifaceted. This section discusses different interpretations of medical terms, such as "orofacial pain," which can vary significantly between a dentist and a neurologist. It introduces the concepts of 'extension' and 'intension' in the context of medical terminology, exploring how these aspects can influence the diagnosis and understanding of medical conditions.<ref>{{cita libro | |||
The | | autore = Porporatti AL | ||
| autore2 = Bonjardim LR | |||
| autore3 = Stuginski-Barbosa J | |||
| autore4 = Bonfante EA | |||
| autore5 = Costa YM | |||
| autore6 = Rodrigues Conti PC | |||
| titolo = Pain from Dental Implant Placement, Inflammatory Pulpitis Pain, and Neuropathic Pain Present Different Somatosensory Profiles | |||
| url = https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28118417 | |||
| opera = J Oral Facial Pain Headache | |||
| anno = 2017 | |||
| ISBN = | |||
| DOI = 10.11607/ofph.1680 | |||
| oaf = | |||
| PMID = 28118417 | |||
}}</ref> | |||
== | ==Ambiguity and Vagueness== | ||
Here, the focus is on the ambiguity and vagueness inherent in medical language, which can complicate the interpretation and application of clinical practice guidelines. The section explains how different meanings of a term like "orofacial pain" can lead to varied diagnostic outcomes and treatment plans.<ref>{{cita libro | |||
| autore = Jääskeläinen SK | |||
| titolo = Differential Diagnosis of Chronic Neuropathic Orofacial Pain: Role of Clinical Neurophysiology | |||
| url = https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31688325 | |||
| volume = | |||
| opera = J Clin Neurophysiol | |||
| anno = 2019 | |||
| ISBN = | |||
| DOI = 10.1097/WNP.0000000000000583 | |||
| oaf = | |||
| PMID = 31688325 | |||
}}</ref> | |||
This section delves into the analogy between medical language and encrypted machine language, suggesting that just as encrypted messages need to be deciphered, medical symptoms and signs require accurate interpretation to avoid misdiagnosis. It discusses the concept of 'epistemic vagueness,' where the lack of clarity in language can lead to diagnostic errors. | |||
<center> <div class="colour-button">[[Special:UserLogin&returnto=Introduction+Page|Read the full chapter]]</div> | Focusing on the decryption of medical language, this section argues for the necessity of understanding both the literal and contextual meanings of medical terms to ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment. It highlights the challenges and complexities involved in interpreting the 'encrypted messages' that symptoms can represent. | ||
==Final Considerations== | |||
The conclusion reiterates the need for a new approach to medical language and diagnostics that focuses less on symptoms and more on the underlying 'encrypted machine language' of diseases. It suggests that a better understanding of this language could lead to improved diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes. | |||
[[Category:Articles about logic of language]]<center> <div class="colour-button">.................[[Special:UserLogin&returnto=Introduction+Page|Read the full chapter]]</div> | |||
</center><blockquote> | </center><blockquote> | ||
== [[Strategic dental topics for authors to subscribe an article]] == | |||
== [[Strategic dental topics for authors to subscribe an article|<small>Strategic dental topics for authors to subscribe an article in Masticationpedia</small>]] == | |||
Medical Language Complexity, Diagnostic Errors in Medicine, Formal Logic in Medical Terminology, Medical Terminology Ambiguity, Interpretation of Medical Terms, Encrypted Machine Language in Medicine, Clinical Case Study in Medicine, Medical Communication Errors, Semantic Ambiguity in Healthcare, Medical Diagnostics Improvement, Medical Language and Patient Care, Interdisciplinary Medical Diagnostics, Medical Terms and Context, Cryptographic Analogies in Medicine | Medical Language Complexity, Diagnostic Errors in Medicine, Formal Logic in Medical Terminology, Medical Terminology Ambiguity, Interpretation of Medical Terms, Encrypted Machine Language in Medicine, Clinical Case Study in Medicine, Medical Communication Errors, Semantic Ambiguity in Healthcare, Medical Diagnostics Improvement, Medical Language and Patient Care, Interdisciplinary Medical Diagnostics, Medical Terms and Context, Cryptographic Analogies in Medicine | ||
{{Bib}} | |||
{{apm}} | |||
Latest revision as of 18:16, 6 May 2024
'Logic of medical language'
Abstract
"The document 'Logic of Medical Language - Masticationpedia' examines the complexities of medical language and its potential for ambiguity, which can lead to misinterpretation and diagnostic errors. By analyzing a clinical case, it stresses the necessity of formal logic in medical terminology to ensure accurate interpretations. The document outlines various examples of how different medical professionals might understand the same condition differently, leading to varied diagnoses.
Key topics covered include the inherent ambiguity in medical language, a detailed clinical case of a patient named Mary Poppins, the concept of 'encrypted machine language' used in brain and medical communications, and the nuanced meanings of medical terms depending on context and user intent. The document concludes with a call for a paradigm shift in medical diagnostics from symptom-based to a more comprehensive understanding of diseases using 'encrypted machine language.'"
Medical language is an extended natural language
This section discusses the semantic challenges in medical language, particularly when traditional natural language intersects with technical medical terminology. It highlights the differences between natural and formal languages, noting that while natural languages evolve organically, formal languages like mathematics are designed with clear rules. The text underlines the ambiguity in terms such as "orofacial pain," which can be interpreted differently depending on the medical specialty involved. This ambiguity is problematic because it can lead to misdiagnosis or conflicting treatments.
The clinical case presented, concerning a patient named Mary Poppins, illustrates the complexities of diagnosing conditions like temporomandibular disorders (TMD) and neuropathic orofacial pain (nOP). The narrative shows how various specialists might interpret the same symptoms differently, leading to multiple diagnoses. The case emphasizes the importance of a multidisciplinary approach and the need for precise language to reduce diagnostic errors.[1][2][3]
Clinical approach
This section uses images to illustrate the clinical manifestations in the patient Mary Poppins, who suffers from orofacial pain and has undergone various medical evaluations that demonstrate the physical changes associated with her condition.
The analysis of 'meaning' in medical terminology is complex and multifaceted. This section discusses different interpretations of medical terms, such as "orofacial pain," which can vary significantly between a dentist and a neurologist. It introduces the concepts of 'extension' and 'intension' in the context of medical terminology, exploring how these aspects can influence the diagnosis and understanding of medical conditions.[4]
Ambiguity and Vagueness
Here, the focus is on the ambiguity and vagueness inherent in medical language, which can complicate the interpretation and application of clinical practice guidelines. The section explains how different meanings of a term like "orofacial pain" can lead to varied diagnostic outcomes and treatment plans.[5]
This section delves into the analogy between medical language and encrypted machine language, suggesting that just as encrypted messages need to be deciphered, medical symptoms and signs require accurate interpretation to avoid misdiagnosis. It discusses the concept of 'epistemic vagueness,' where the lack of clarity in language can lead to diagnostic errors.
Focusing on the decryption of medical language, this section argues for the necessity of understanding both the literal and contextual meanings of medical terms to ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment. It highlights the challenges and complexities involved in interpreting the 'encrypted messages' that symptoms can represent.
Final Considerations
The conclusion reiterates the need for a new approach to medical language and diagnostics that focuses less on symptoms and more on the underlying 'encrypted machine language' of diseases. It suggests that a better understanding of this language could lead to improved diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes.
Strategic dental topics for authors to subscribe an article in Masticationpedia
Medical Language Complexity, Diagnostic Errors in Medicine, Formal Logic in Medical Terminology, Medical Terminology Ambiguity, Interpretation of Medical Terms, Encrypted Machine Language in Medicine, Clinical Case Study in Medicine, Medical Communication Errors, Semantic Ambiguity in Healthcare, Medical Diagnostics Improvement, Medical Language and Patient Care, Interdisciplinary Medical Diagnostics, Medical Terms and Context, Cryptographic Analogies in Medicine
Bibliography & references
- ↑ Tanaka E, Detamore MS, Mercuri LG, «Degenerative disorders of the temporomandibular joint: etiology, diagnosis, and treatment», in J Dent Res, 2008».
PMID:18362309
DOI:10.1177/154405910808700406- ↑ Roberts WE, Stocum DL, «Part II: Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)-Regeneration, Degeneration, and Adaptation», in Curr Osteoporos Rep, 2018».
PMID:29943316
DOI:10.1007/s11914-018-0462-8- ↑ Lingzhi L, Huimin S, Han X, Lizhen W, «MRI assessment and histopathologic evaluation of subchondral bone remodeling in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: a retrospective study», in Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2018».
PMID:30122441
DOI:10.1016/j.oooo.2018.05.047- ↑ Porporatti AL, Bonjardim LR, Stuginski-Barbosa J, Bonfante EA, Costa YM, Rodrigues Conti PC, «Pain from Dental Implant Placement, Inflammatory Pulpitis Pain, and Neuropathic Pain Present Different Somatosensory Profiles», in J Oral Facial Pain Headache, 2017».
PMID:28118417
DOI:10.11607/ofph.1680- ↑ Jääskeläinen SK, «Differential Diagnosis of Chronic Neuropathic Orofacial Pain: Role of Clinical Neurophysiology», in J Clin Neurophysiol, 2019».
PMID:31688325
DOI:10.1097/WNP.0000000000000583Masticationpedia is a charity, a not-for-profit organization operating in dentistry medical research,
particularly focusing on the field of the neurophysiology of the masticatory system