Complex Systems/de
Nach den vorangegangenen Kapiteln sollten wir nun erkennen können, dass sowohl in der modernen Physik als auch in der Biologie ein „komplexes System“ ein dynamisches Mehrkomponentensystem ist, das aus verschiedenen Teilsystemen besteht, die typischerweise miteinander interagieren. Solche Systeme werden typischerweise durch "ganzheitliche" Untersuchungsmethoden oder als "vollständige" Berechnung des Verhaltens der einzelnen Subsysteme zusammen mit ihren gegenseitigen Wechselwirkungen untersucht; diese können eher analytisch durch mathematische Modelle beschrieben werden als auf "reduktionistische" Weise (dh durch Zerlegen und Analysieren des Systems in seine Komponenten).. Typisch für komplexe Systeme sind die Konzepte der Selbstorganisation und „Emerging Behaviour“.
In diesem Kapitel werden wir einige Inhalte zugunsten dieser eher stochastischen und komplexeren Vision der neuromotorischen Funktionen des Kausystems aufdecken.
Vorüberlegung
In den letzten Jahren konzentrierten sich parallele Entwicklungen in verschiedenen Disziplinen auf das, was als "Konnektivität" bezeichnet wurde, ein Konzept, das verwendet wird, um die "komplexen Systeme" zu verstehen und zu beschreiben.. Die Konzeptualisierungen und Funktionalisierungen von Konnektivität haben sich innerhalb ihrer Disziplingrenzen weit entwickelt, aber es gibt deutliche Ähnlichkeiten in diesem Konzept und in seiner Anwendung über die Disziplinen hinweg. Jede Implementierung des Konnektivitätskonzepts beinhaltet jedoch sowohl ontologische als auch erkenntnistheoretische Einschränkungen, die uns zu der Frage veranlassen, ob es eine Art oder eine Reihe von Konnektivitätsansätzen gibt, die auf alle Disziplinen angewendet werden könnten. In diesem Aufsatz untersuchen wir vier ontologische und erkenntnistheoretische Herausforderungen bei der Verwendung von Konnektivität zum Verständnis komplexer Systeme aus der Sicht sehr unterschiedlicher Disziplinen.
Im Kapitel „Konnektivität und komplexe Systeme“ stellen wir abschließend das Konzept von vor:
- Definieren der grundlegenden Einheit für das Studium der Konnektivität;
- Trennung der strukturellen Konnektivität von der funktionellen Konnektivität;
- Verständnis für aufkommendes Verhalten; und
- Konnektivität messen.
Wir müssen nun das komplexe Profil der Kaufunktion betrachten, um von „Konnektivität“ sprechen zu können.[1]
Erst in späteren Zeiten wurde die Bedeutung der Kaufunktion als komplexes System deutlich; deutlich wird es durch seine Interaktion mit einer Vielzahl anderer Nervenzentren und -systeme (ZNS), die ebenfalls funktionell weit entfernt sind.[2]. Die Kaufunktion wurde in der Tat immer als periphere und isolierte Funktion in Bezug auf die Phonetik und das Kauen betrachtet. Dieser Interpretation folgend gab es unzählige Sichtweisen, die sich ausschließlich auf die Diagnose und Rehabilitation von Kauen im Oberkiefer konzentrierten und konzentrieren, indem sie jede multistrukturelle Korrelation ausschlossen.
Diese Art der Herangehensweise bezeichnet einen klaren „Reduktionismus“ in den Inhalten des Systems selbst: in der Biologie ist es realistischer, die Funktionalität von Systemen wie "Komplexen Systemen" zu betrachten, die nicht linear funktionieren. Diese Systeme verwenden einen stochastischen Ansatz, bei dem die Interaktion der verschiedenen Bestandteile ein „emergentes Verhalten“ (EB) erzeugt.[3] of the same system.[4]
Das paradigmatische Ergebnis kehrt die Tendenz um, das Kausystem als ein einfaches kinematisches Organ zu betrachten, und geht weit über das traditionelle mechanistische Verfahren der klassischen Gnathologie hinaus.
Dieser Aspekt führt auch eine Art indeterministisches Profil biologischer Funktionen ein, in dem sich die Funktion eines Systems als ein Netzwerk mehrerer verwandter Elemente darstellt. Zusätzlich zur Interpretation seines Zustands sollte dieses System von außen stimuliert werden, um die evozierte Reaktion zu analysieren, wie es für indeterministische Systeme typisch ist.[6]
Es ist daher unerlässlich, von einem einfachen und linearen Modell der Zahnklinik zu einem stochastischen komplexen Modell der Kauneurophysiologie zu wechseln.
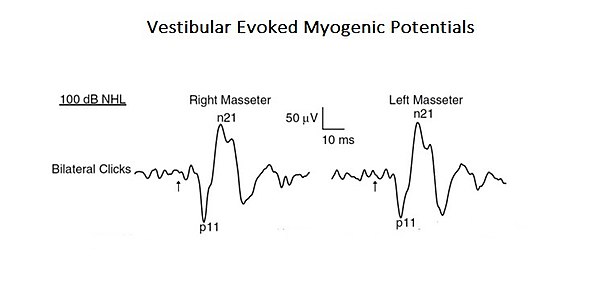
Als Bestätigung dieses komplexeren und integrierten Ansatzes zur Interpretation der Kaufunktionen wird hier eine Studie vorgestellt, in der das Profil eines „Neural Complex System“ auftaucht. In der erwähnten Studie wurde die organische und funktionelle Verbindung des vestibulären Systems mit dem trigeminalen System analysiert. [7]. Akustische Reize können EMG-Reflexantworten im Massetermuskel hervorrufen, die als vestibuläre evozierte myogene Potenziale (VEMPs) bezeichnet werden.. Auch wenn diese Ergebnisse bisher auf die Aktivierung der cochleären Rezeptoren (hohe Schallintensität) zurückgeführt wurden, können diese auch die vestibulären Rezeptoren aktivieren. Da anatomische und physiologische Studien sowohl bei Tieren als auch bei Menschen gezeigt haben, dass Kaumuskeln ein Ziel für vestibuläre Eingänge sind, haben die Autoren dieser Studie den vestibulären Beitrag für die Masseterreflexe neu bewertet. Dies ist ein typisches Beispiel für ein komplexes System auf Basisebene, da es nur aus zwei kranialen Nervensystemen besteht, aber gleichzeitig durch Aktivierung mono- und polysynaptischer Schaltkreise interagiert (Abbildung 1).
An dieser Stelle wäre es angebracht, einige Themen im Zusammenhang mit den oben genannten Konzepten einzuführen, die die Begründung des Masticationpedia-Projekts verdeutlichen würden. Dies würde die Kapitel einführen, die den Kern des Projekts bilden.
Daher ist das Objekt:
diese werden um zusätzliche wesentliche Themen erweitert, wie z. B. die „Segmentierung des Trigeminusnervensystems“ im letzten Kapitel „Außergewöhnliche Wissenschaft“..»
Kauen und kognitive Prozesse
In den letzten Jahren war das Kauen ein Diskussionsthema über die Erhaltungs- und Unterstützungseffekte der kognitiven Leistungsfähigkeit.
Eine elegante Studie, die durch fMR und Positronen-Emissions-Tomographie (PET) durchgeführt wurde, hat gezeigt, dass das Kauen zu einer Erhöhung des kortikalen Blutflusses führt und den zusätzlichen somatosensorischen Kortex, Motormotor und Insular sowie das Striatum aktiviert , den Thalamus und das Kleinhirn. Das Kauen direkt vor der Durchführung einer kognitiven Aufgabe erhöht den Sauerstoffgehalt im Blut (FETT im fMRT-Signal) im präfrontalen Kortex und im Hippocampus, wichtige Strukturen, die am Lernen und Gedächtnis beteiligt sind, wodurch die Leistungsaufgabe verbessert wird.[8] Frühere epidemiologische Studien haben gezeigt, dass eine reduzierte Anzahl von Restzähnen, eine inkongruente Verwendung von Prothesen und eine eingeschränkte Entwicklung der Unterkieferkraft in direktem Zusammenhang mit der Entwicklung von Demenz stehen, was die Annahme weiter stützt, dass Kauen zur Aufrechterhaltung kognitiver Funktionen beiträgt.[9].
Eine kürzlich durchgeführte Studie hat weitere Beweise für die Interaktion zwischen Kauprozessen, Lernen und Gedächtnis geliefert und sich auf die Funktion des Hippocampus konzentriert, die für die Bildung neuer Erinnerungen unerlässlich ist[10]. Eine okklusale Disharmonie, wie z. B. Zahnverlust und Zunahme der vertikalen okklusalen Dimension, verursacht Bruxismus oder Schmerzen der Kaumuskulatur und temporomandibuläre Störungen (TMDs).[11][12]. Um die beeinträchtigte Funktion des Hippocampus in einer reduzierten Situation oder abnormen Kaufunktion zu beschreiben, verwendeten die Autoren daher ein Tiermodell (Mäuse) namens „Molarless Senescence-Accelerated Prone“ (SAMP8), um eine Parallelität zum Menschen herzustellen. Bei SAMP8-Mäusen, bei denen die Okklusion modifiziert wurde, zeigte die Erhöhung der okklusalen vertikalen Dimension von etwa 0,1 mm mit Dentalmaterialien, dass die okklusale Disharmonie Lernen und Gedächtnis stört. Diese Tiere zeigten ein altersabhängiges Defizit im Raumlernen an Morris’ Wasser. [13][14]
Die Erhöhung der vertikalen Dimension des Bisses in SAMP8-Mäusen verringert die Anzahl der Pyramidenzellen[14] und die Anzahl ihrer dendritischen Stacheln.[15] Es erhöht auch die Hypertrophie und Hyperplasie der fibrillären Proteinsäure in Astrozyten in den Regionen des CA1- und CA3-Hippocampus.[16]. Bei Nagetieren und Affen okklusale Disharmonien, die durch eine Erhöhung der vertikalen Dimension mit Acrylerhöhungen an den Schneidezähnen induziert werden[17][18] oder Das Einsetzen der Bissebene in den Kiefer ist mit erhöhten Cortisolspiegeln im Urin und erhöhten Corticosteronspiegeln im Plasma verbunden, was darauf hindeutet, dass okklusale Disharmonie auch eine Stressquelle ist.
Zur Stützung dieser Annahme zeigen SAMP8-Mäuse mit Lerndefiziten einen deutlichen Anstieg der Plasmaspiegel von Corticosteron[12] und subregulation of GR and GRmRNA of the hippocampus. The occlusal disharmony also affects catecholaminergic activity. Alternating the closure of the bite by inserting an acrylic bite-plane on the lower incisors leads to an increase in levels of dopamine and noradrenaline in the hypothalamus and the frontal cortex[17][19], and decreases in thyroxinaydroxylase, GTP cyclohydrochloride, and immunoreactive serotonin in the cerebral cortex and the caudate nucleus, in the nigra substance, in the locus ceruleus, and in the dorsal raphe nucleus, which are similar to chronic stress-induced changes.[20] These changes in the catecolaminergic and serotonergic systems, induced by occlusal disharmonies, clearly affect the innervation of the hippocampus. The conditions of increasing the vertical dimension alter neurogenesis and lead to apoptosis in the ippocampal gyrus by decreasing the expression of the ippocampal brain derived from neurotrophic factors: all this could contribute to the changes in observed learning in animals with occlusal disharmony.[10]
Brainstem and Mastication
The brainstem district is a relay area that connects the upper centres of the brain, the cerebellum, and the spinal cord, and provides the main sensory and motor innervation of the face, head, and neck through the cranial nerves.
This plays a determining role in regulation of respiration, locomotion, posture, balance, excitement (including intestinal control, bladder, blood pressure, and heart rate). It is responsible for regulating numerous reflexes, including swallowing, coughing, and vomiting. The brainstem is controlled by higher Cerebral Centers from cortical and subcortical regions, including the Basal Ganglia Nuclei and Diencephal, as well as feedback loops from the cerebellum and spinal cord. Neuromodulation can be achieved by the ‘classical’ mode of glutammatergic neurotransmitters and GABA (gamma-amino butyric acid) through a primary excitation and inhibition of the ‘anatomical network’, but can also be achieved through the use of transmitters acting on G-proteins. These neuromodulators include the monoamine (serotonine, noradrenaline, and dopamine) acetylcholine, as also glutamate and GABA. In addition, not only do neuropeptides and purines act as neuromodulators: so do other chemical mediators too, like Growth Factors which might have similar actions.[21]
The neural network described above does not end with the only correlation between trigeminal somatosensory centres and other motor areas but also strays into the amigdaloidei processes through a correlation with the trigeminal brainstem area. The amygdala becomes active from fear, playing an important role in the emotional response to life-threatening situations. When lab rats feel threatened, they respond by biting ferociously. The force of the bite is regulated by the motor nuclei of the trigeminal system and trigeminal brainstem Me5.The Me5 transmits proprioceptive signals from the Masticatory muscles and parodontal ligaments to trigeminal nuclei and motors. Central Amygdaloid Nucleus (ACe) projections send connections to the trigeminal motor nucleus and reticular premotor formation and directly to the Me5.
To confirm this, in a study conducted among mice, the neurons in the Central Amigdaloide nucleus (ACe) were marked after the injection of a retrograde tracer(Fast Blue), in the caudal nucleus of the Me5, indicating that the Amigdaloians send direct projections to the Me5, and suggest that the amygdala regulates the strength of the bite by modifying the neuronal activity in the Me5 through a neural facilitation.[22]
Modifying occlusal ratios can alter oral somatosensory functions and the rehabilitative treatments of the Masticatory system should restore somatosensory functions. However, it is unclear why some patients fail to adapt to the masticatory restoration, and sensomotor disorders remain. At first, they would seem to be structural changes, not just functional ones. The primary motor cortex of the face is involved in the generation and control of facial gold movements and sensory inputs or altered motor functions, which can lead to neuroplastic changes in the M1 cortical area.[10][23]
Conclusive Considerations
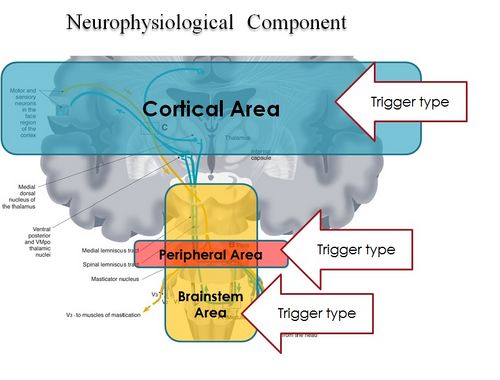
In conclusion, it is clear from the premise, that the Masticatory system should be considered not certainly as a system simply governed by mechanical laws, but as a "Complex System" of indeterministic type, where one can quantify the "Emerging Behavior" only after stimulating it and then analysing the response evoked (Figure 2). The Neuronal System also dialogues with its own encrypted machine language (potential action and ionic currents) and, therefore, it is not possible to interpret the symptoms referred to by the patient through natural language.
This concept deepens knowledge of the state of health of a system because it elicits an answer from inside the network — or, at least, from a large part of it — by allocating normal and/or abnormal components of the various nodes of the network. In scientific terms, it also introduces a new paradigm in the study of the Masticatory System: the "Neuro Gnathology Function", that we will meet in due course in the chapter ‘Extraordinary Science’.
Currently, the interpretation of the Emergent Behavior of the Mastication system in dentistry is performed only by analysing the voluntary valley response, through electromyographic recordings ‘EMG interference pattern’, and radiographic and axographic tests (replicators of mandibular movements). These can only be considered descriptive tests.
The paradigm of gnathological descriptive tests faced a crisis years ago: despite an attempt to reorder the various axioms, schools of thought, and clinical-experimental strictness in the field of Temporomandibular Disorders (through the realization of a protocol called "Research Diagnostic Criteria" RDC/TMDs), this paradigm has not yet come to be accepted because of the scientific-clinical incompleteness of the procedure itself. It deserves, however, a particular reference to the RDC/TMD, at least for the commitment that was carried out by the authors and, at the same time, to scroll the limits.
The RDC/TMD protocol was designed and initialized to avoid the loss of ‘standardized diagnostic criteria’ and evaluate a diagnostic standardization of empirical data at disposition. This protocol was supported by the National Institute for Dental Research (NIDR) and conducted at the University of Washington and the Group Health Corporative of Puget Sound, Seattle, Washington. Samuel F. Dworkin, M. Von Korff, and L. LeResche were the main investigators[24].
To arrive at the formulation of the protocol of the ‘RDC’, a review of the literature of diagnostic methods in rehabilitative dentistry and TMDs, and subjected to validation and reproducibility, has been made. Taxonomic systems were taken into account by Farrar (1972)[25][26], Eversole and Machado (1985)[27], Bell (1986)[28], Fricton (1989)[29], American Academy of Craniomandibular Disorders (AACD) (1990)[30], Talley (1990)[31], Bergamini and Prayer-Galletti (1990)[32], Truelove (1992)[33], and compared them by granting them to a set of assessment criteria. The evaluation criteria were split into two categories that involve methodological considerations and clinical considerations.
The end of the research came to the elimination, due to a lack of scientific and clinical validation, of a series of instrumental diagnostic methodologies like interferential electromyography (EMG Interference Pattern), Pantography, X-ray diagnostics, etc. These will be described in more detail in the next editions of Masticationpedia. This first target was, therefore, the scientific request of an "objective data"' and not generated by opinions, schools of thought or subjective evaluations of the phenomenon’. During the Workshop of the International Association for Dental Research (IADR) of 2008, preliminary results of the RDC/TMDs were presented in the endeavour to validate the project.
The conclusion was that, to achieve a review and simultaneous validation of [RDC/TMD], it is essential that the tests should be able to make a differential diagnosis between TMD patients with pain and subjects without pain, and above all, discriminate against patients with TMD pain from patients with orofacial pain without TMD.[34]
This last article, reconsidering pain as an essential symptom for the clinical interpretation, puts all the neurophysiological phenomenology in the game, not just this. To move more easily at ease in this medical branch, a different scientific-clinical approach is required, one that widens the horizons of competence in fields such as bioengineering and neurobiology.
It is, therefore, essential to focus attention on how to take trigeminal electrophysiological signals in response to a series of triggers evoked by an electrophysiological device, treating data and determining an organic-functional value of the trigeminal and masticatory systems as anticipated by Marom Bikson and coll. in their «Electrical stimulation of cranial nerves in cognition and disease».
We should think of a system that unifies the mastication and neurophysiological functions by introducing a new term: "Neuro-Gnathological Functions"
which will be the object of a dedicated chapter.
- ↑ Turnbull L, Hütt MT, Ioannides AA, Kininmonth S, Poeppl R, Tockner K, Bracken LJ, Keesstra S, Liu L, Masselink R, Parsons AJ, «Connectivity and complex systems: learning from a multi-disciplinary perspective», in Appl Netw Sci, 2018».
PMID:30839779 - PMCID:PMC6214298
DOI:10.1007/s41109-018-0067-2
This is an Open Access resource! - ↑ Viggiano A, Manara R, Conforti R, Paccone A, Secondulfo C, Lorusso L, Sbordone L, Di Salle F, Monda M, Tedeschi G, Esposito F, «Mastication induces long-term increases in blood perfusion of the trigeminal principal nucleus», in Neuroscience, Elsevier, 2015».
PMID:26477983
DOI:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.10.017 - ↑ Florio T, Capozzo A, Cellini R, Pizzuti G, Staderini EM, Scarnati E, «Unilateral lesions of the pedunculopontine nucleus do not alleviate subthalamic nucleus-mediated anticipatory responding in a delayed sensorimotor task in the rat», in Behav Brain Res, 2001».
PMID:11704255
DOI:10.1016/s0166-4328(01)00248-0 - ↑ de Boer RJ, Perelson AS, «Size and connectivity as emergent properties of a developing immune network», in J Theor Biol, 1991».
PMID:2062103
DOI:10.1016/s0022-5193(05)80313-3 - ↑ Iyer-Biswas S, Hayot F, Jayaprakash C, «Stochasticity of gene products from transcriptional pulsing», in Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys, 2009».
PMID:19391975
DOI:10.1103/PhysRevE.79.031911
This is an Open Access resource! - ↑ Lewis ER, MacGregor RJ, «On indeterminism, chaos, and small number particle systems in the brain», in J Integr Neurosci, 2006».
PMID:16783870
DOI:10.1142/s0219635206001112 - ↑ Deriu F, Ortu E, Capobianco S, Giaconi E, Melis F, Aiello E, Rothwell JC, Tolu E, «Origin of sound-evoked EMG responses in human masseter muscles», in J Physiol, 2007».
PMID:17234698 - PMCID:PMC2075422
DOI:10.1113/jphysiol.2006.123240
This is an Open Access resource! - ↑ Yamada K, Park H, Sato S, Onozuka M, Kubo K, Yamamoto T, «Dynorphin-A immunoreactive terminals on the neuronal somata of rat mesencephalic trigeminalnucleus», in Neurosci Lett, Elsevier Ireland, 2008».
PMID:18455871
DOI:10.1016/j.neulet.2008.04.030 - ↑ Kondo K, Niino M, Shido K, «Dementia. A case-control study of Alzheimer's disease in Japan - significance of life-styles», 1994».
PMID:7866485
DOI:10.1159/000106741 - ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Kubo KY, Ichihashi Y, Kurata C, Iinuma M, Mori D, Katayama T, Miyake H, Fujiwara S, Tamura Y, «Masticatory function and cognitive function», in Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn, 2010».
PMID:21174943
DOI:10.2535/ofaj.87.135
This is an Open Access resource! - ↑ Christensen J, «Effect of occlusion-raising procedures on the chewing system», in Dent Pract Dent Rec, 1970».
PMID:5266427 - ↑ 12.0 12.1 Ichihashi Y, Arakawa Y, Iinuma M, Tamura Y, Kubo KY, Iwaku F, Sato Y, Onozuka M, «Occlusal disharmony attenuates glucocorticoid negative feedback in aged SAMP8 mice», in Neurosci Lett, 2007».
PMID:17928141
DOI:10.1016/j.neulet.2007.09.020 - ↑ Arakawa Y, Ichihashi Y, Iinuma M, Tamura Y, Iwaku F, Kubo KY, «Duration-dependent effects of the bite-raised condition on hippocampal function in SAMP8 mice», in Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn, 2007».
PMID:18186225
DOI:10.2535/ofaj.84.115
This is an Open Access resource! - ↑ 14.0 14.1 Kubo KY, Yamada Y, Iinuma M, Iwaku F, Tamura Y, Watanabe K, Nakamura H, Onozuka M, «Occlusal disharmony induces spatial memory impairment and hippocampal neuron degeneration via stress in SAMP8 mice», in Neurosci Lett, Elsevier Ireland, 2007».
PMID:17207572
DOI:10.1016/j.neulet.2006.12.020 - ↑ Kubo KY, Kojo A, Yamamoto T, Onozuka M, «The bite-raised condition in aged SAMP8 mice induces dendritic spine changes in the hippocampal region», in Neurosci Lett, 2008».
PMID:18614288
DOI:10.1016/j.neulet.2008.05.027 - ↑ Ichihashi Y, Saito N, Arakawa Y, Kurata C, Iinuma M, Tamura Y, Iwaku F, Kubo KY, «The bite-raised condition in aged SAMP8 mice reduces the expression of glucocorticoid receptors in the dorsal and ventral hippocampus», in Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn, 2008».
PMID:18464530
DOI:10.2535/ofaj.84.137
This is an Open Access resource! - ↑ 17.0 17.1 Areso MP, Giralt MT, Sainz B, Prieto M, García-Vallejo P, Gómez FM, «Occlusal disharmonies modulate central catecholaminergic activity in the rat», in J Dent Res, 1999».
PMID:10371243
DOI:10.1177/00220345990780060301 - ↑ Yoshihara T, Matsumoto Y, Ogura T, «Occlusal disharmony affects plasma corticosterone and hypothalamic noradrenaline release in rats», in J Dent Res, 2001».
PMID:11808768
DOI:10.1177/00220345010800121301 - ↑ Gómez FM, Areso MP, Giralt MT, Sainz B, García-Vallejo P, «Effects of dopaminergic drugs, occlusal disharmonies, and chronic stress on non-functional masticatory activity in the rat, assessed by incisal attrition», in J Dent Res, 1998».
PMID:9649174
DOI:10.1177/00220345980770061001 - ↑ Feldman S, Weidenfeld J, «Glucocorticoid receptor antagonists in the hippocampus modify the negative feedback following neural stimuli», in Brain Res, Elsevier Science B.V., 1999».
PMID:10064785
DOI:10.1016/s0006-8993(99)01054-9 - ↑ Mascaro MB, Prosdócimi FC, Bittencourt JC, Elias CF, «Forebrain projections to brainstem nuclei involved in the control of mandibular movements in rats», in Eur J Oral Sci, 2009, São Paulo, Brazil».
PMID:20121930
DOI:10.1111/j.1600-0722.2009.00686.x - ↑ Shirasu M, Takahashi T, Yamamoto T, Itoh K, Sato S, Nakamura H, «Direct projections from the central amygdaloid nucleus to the mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus in rats», in Brain Res, 2011».
PMID:21640334
DOI:10.1016/j.brainres.2011.05.026 - ↑ Avivi-Arber L, Lee JC, Sessle BJ, «Dental Occlusal Changes Induce Motor Cortex Neuroplasticity», in J Dent Res, International & American Associations for Dental Research, 2015, Toronto, Canada».
PMID:26310722
DOI:10.1177/0022034515602478 - ↑ Dworkin SF, Huggins KH, Wilson L, Mancl L, Turner J, Massoth D, LeResche L, Truelove E, «A randomized clinical trial using research diagnostic criteria for temporomandibular disorders-axis II to target clinic cases for a tailored self-care TMD treatment program», in J Orofac Pain, 2002».
PMID:11889659 - ↑ Farrar WB, «Differentiation of temporomandibular joint dysfunction to simplify treatment», in J Prosthet Dent, 1972».
PMID:4508486
DOI:10.1016/0022-3913(72)90113-8 - ↑ Farrar WB, «Controversial syndrome», in J Am Dent Assoc, Elsevier Inc, 1972».
PMID:4503595
DOI:10.14219/jada.archive.1972.0286 - ↑ Eversole LR, Machado L, «Temporomandibular joint internal derangements and associated neuromuscular disorders», in J Am Dent Assoc, 1985».
PMID:3882811
DOI:10.14219/jada.archive.1985.0283 - ↑ Storum KA, Bell WH, «The effect of physical rehabilitation on mandibular function after ramus osteotomies», in J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 1986».
PMID:3456031
DOI:10.1016/0278-2391(86)90188-6 - ↑ Schiffman E, Anderson G, Fricton J, Burton K, Schellhas K, «Diagnostic criteria for intraarticular T.M. disorders», in Community Dent Oral Epidemiol, 1989».
PMID:2791516
DOI:10.1111/j.1600-0528.1989.tb00628.x - ↑ Phillips DJ Jr, Gelb M, Brown CR, Kinderknecht KE, Neff PA, Kirk WS Jr, Schellhas KP, Biggs JH 3rd, Williams B, «Guide to evaluation of permanent impairment of the temporomandibular joint», in Cranio, American Academy of Head, Neck and Facial Pain; American Academy of Orofacial Pain; American Academy of Pain Management; American College of Prosthodontists; American Equilibration Society and Society of Occlusal Studies; American Society of Maxillofacial Surgeons; American Society of Temporomandibular Joint Surgeons; International College of Cranio-mandibular Orthopedics; Society for Occlusal Studies, 1997».
PMID:9586521 - ↑ Talley RL, Murphy GJ, Smith SD, Baylin MA, Haden JL, «Standards for the history, examination, diagnosis, and treatment of temporomandibular disorders(TMD): a position paper», in Cranio, American Academy of Head, Neck and Facial Pain, 1990».
PMID:2098190
DOI:10.1080/08869634.1990.11678302 - ↑ Prayer Galletti S, Colonna MT, Meringolo P, «The psychological aspects of craniocervicomandibular pain dysfunction pathology», in Minerva Stomatol, 1990».
PMID:2398856 - ↑ Truelove EL, Sommers EE, LeResche L, Dworkin SF, Von Korff M, «Clinical diagnostic criteria for TMD. New classification permits multiple diagnoses», in J Am Dent Assoc, 1992».
PMID:1290490
DOI:10.14219/jada.archive.1992.0094 - ↑ Lobbezoo F, Visscher CM, Naeije M, «Some remarks on the RDC/TMD Validation Project: report of an IADR/Toronto-2008 workshop discussion», in J Oral Rehabil, Academic Centre for Dentistry Amsterdam (ACTA), 2010, Amsterdam, The Netherlands».
PMID:20374440
DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2842.2010.02091.x
particularly focusing on the field of the neurophysiology of the masticatory system