Encrypted code: Bilateral Motor Evoked Potentials of trigeminal root
The subject, .
Introduction
Bruxism (4398), trigeminal system (29), abnormality ( 5), excitability ( 3)The excitability of the trigeminal motor system in sleep bruxism: a transcranial magnetic stimulation and brainstem reflex study
Diagnostic sequences
1st Step: CNN Sequence
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29696497/ (gait AND tendon reflex AND masseter)
- Coherence Demarcator:
- 1st loop open:
- 2st loop open:
- 3st loop open:
Potenziali Evocati Motori della radice trigeminale
Potenziali Evocati Motori della radice trigeminale
To simplify the examination, the rcMIR was evoked by electrically stimulating the left side only. The EMG responses correspond to the EMG tracings of the right masseter (Ch1) and left masseter (Ch2). Thus, on the traces, each marker indicates the channel number, while the letters indicate the sequences of latencies.
- The S1 stimulus splits the acquisition into pre and post analysis and generates the SPs and the AI.
- The stimulus S2 delivered 150 ms from S1, called interstimulus (IS), evokes the second SP sequence and the IA.
- The SP of S1 and S2 are determined automatically by the software which positions the markers on the first and last minimum value elaborated on the traces for the generation of SP1 and SP2, and contextually calculates their duration. The IA duration is calculated between the last minimum value of SP1 and the first minimum value of SP2.
In the tested subject the S2 stimulus was able to evoke both SPs, while in a normal subject the S2 stimulus is normally able to evoke only the SP1 or at most one SP2 of reduced duration. As shown in Table 2, the duration of S2-evoked SP1 was found to be very stable, with no significant differences in the duration of S1-generated SP1 (Δ= -1ms for Ch1 and Δ= -2 ms for Ch2) while the from S2 on the right and left masseter (61 ms and 54 ms, respectively) was longer than that evoked by S1 (39 ms and 35 ms, respectively). The differences were +22 ms for Ch1 (right masseter) and +19 ms for Ch2 (left masseter). Consequently, the duration of the AI showed clear differences between S2 and S1. The duration of the S2-evoked AI was 12 ms vs. 23 ms of S1 stimulus for the right masseter (Ch1) and 17 ms vs 30 ms of S1 for the left masseter (Ch2) with a difference between the responses evoked by S2 minus S1 of -11 ms and -13 ms, respectively.
3rd Step: brain MNR
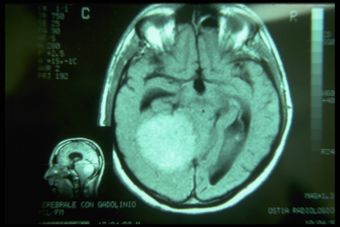
MRI of the brain, using Turbo Spin Echo, Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery, and Gradient Echo sequences, was conducted before and after intravenous administration of contrast medium. Results showed the presence of a roundish area of approximately 1.5 cm in diameter located in the vicinity of the quadrigeminal cistern at the level of the pineal gland. There was also a slight dilation of the supratentorial ventricular system, which appeared in the axis and was most evident in the proximity of the temporal horns, with a periventricular rim with a transependymal fluid absorption phenomenon.[1] The signal characteristics of the formation suggested a provisional diagnosis of pineal cavernoma. (Figures 2 and 3)
Final considerations
As we can see from the 'Visual Cognitive gallery', the neurological context is enriched by the contribution deriving from the decryption of the machine language through the rcMIR () test to definitively close the diagnosis with the MR report (). The diagnostic model Masticationpedia not only supports the doctor in complex diagnoses but above all it is an element of implementation of our basic knowledge . It will be useful to represent this cognitive interpretation by correlating it to the images of the assertions of the neurological context.
Discussion
- ↑ Peter H Yang, Alison Almgren-Bell, Hongjie Gu, Anna V Dowling, Sangami Pugazenthi, Kimberly Mackey, Esther B Dupépé, Jennifer M Strahle. Etiology- and region-specific characteristics of transependymal cerebrospinal fluid flow. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2022 Aug 12;1-11. doi: 10.3171/2022.7.PEDS2246. Online ahead of print.